7 stages of periodontitis treatment: is it possible to get rid of the problem forever?
Periodontitis is an inflammation of periodontal tissues, which includes the teeth, ligaments, cementum and gums. Periodontitis as a disease is a minor inflammation of the gums, the main cause of which is neglect of oral hygiene. If with gingivitis the inflammation spreads exclusively to the soft mucous membranes, then with periodontitis the ligaments that hold the teeth in the sockets are affected. This is why in 90% of cases when this disease is diagnosed, tooth mobility is observed, which eventually leads to their loss.
This is what tartar and gum recession look like with gum diseasewebsite presents a selection of the most modern methods of treating periodontitis and reminds that it is impossible to cure the disease, but it is quite possible to reduce its manifestations and reduce the risk of relapses.
Periodontitis: symptoms and causes of the disease
Periodontitis manifests itself in the form of bleeding gums, and it can even be constant, without any external influence. Due to the inflammatory process, cavities very often form, the so-called gingival or periodontal pockets, in which the mucous membrane moves away from the tooth - food, microbes and plaque accumulate in such cavities. The contents of the pockets can rot, which causes a strong bad breath. Due to inflammation of the ligamentous apparatus, tooth mobility occurs - this usually occurs at an advanced, that is, chronic generalized stage of the disease, and progresses as the inflammation spreads.
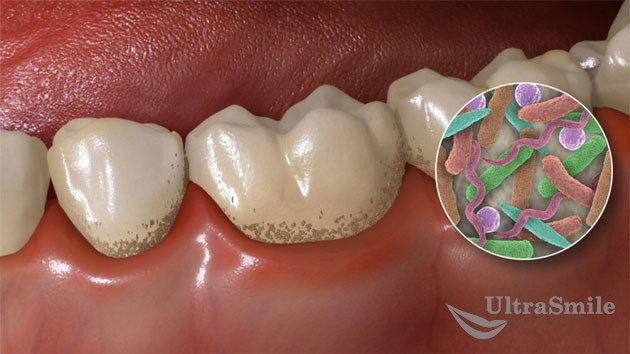 Bacteria are the main cause of gum inflammation
Bacteria are the main cause of gum inflammation The main cause of periodontitis is poor oral hygiene, which results in the formation of dental deposits (plaque and tartar), causing inflammation of the gums and all tissues around the tooth. Other factors include injury to the gums by dentures or incorrectly installed fillings, mechanical burns, and malocclusion - in all these cases, conditions are created for the accumulation of bacteria that cause inflammation of damaged gums. Common factors can also be identified as a separate group - these are various diseases of the body: diabetes mellitus, disorders of the endocrine system or gastrointestinal tract, a general decrease in immunity, changes in hormonal levels (elderly people and adolescents, pregnant and lactating women).
Treatment of periodontitis: 7 procedures that will help get rid of the problem
Unfortunately, it is impossible to cure periodontitis completely, to the point of completely healthy gums. But this does not mean that the disease does not need to be treated. The procedures below, if carried out in combination, will significantly improve the condition of the gums, relieve inflammation and even extend the life of mobile teeth. And the sooner treatment is started, the higher the chance that the teeth will last for several more decades.
It is customary to distinguish several stages of the disease. Localized affects one or several teeth, generalized spreads to a large number of elements of the dentition. Both can proceed either brightly, with all the symptoms, or without noticeable manifestations - when they become chronic.
Generalized chronic periodontitis (often progresses to periodontal disease) is an incurable disease. In this case, the best thing the patient can do for himself is to remove loose teeth and decide on implantation. The implant models used today prevent the process of gum inflammation and are fixed bypassing the atrophied areas of the bone. They also provide a high level of quality of life, allowing you to smile without embarrassment and eat any food, while this is not possible with bad teeth.
So, let's look at how such an unpleasant and even dangerous disease is treated.
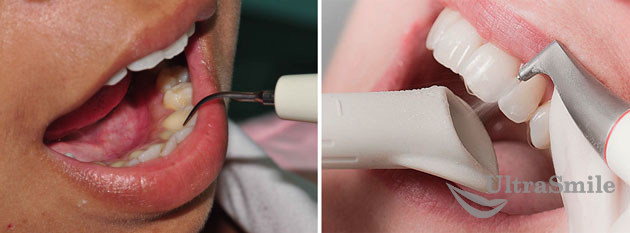
Removing plaque and tartar is the most important thing to do. It is the deposits that provoke inflammatory processes. By the way, professional cleaning of the oral cavity should also be carried out for the sake of prevention - 1-2 times a year. The following methods are used for this:
- Ultrasound: the most common method for removing plaque. Through a special tip, ultrasonic vibrations along with a stream of water are applied to the teeth and gums. Ultrasound literally breaks the hard stone, and a stream of water washes it out of the mouth. Today, the most progressive clinics use Vector or Varius devices for these purposes. In some situations, they even allow you to do without surgical curettage of the gums,
- Air Flow: This technology involves sandblasting dental plaque using abrasive particles, air and water. Under high pressure, a stream is directed through the tip of the device onto the teeth and gums, effectively removing deposits, especially from hard-to-reach places. Often used in combination with ultrasound,
- manual removal: instruments with a hook at the end are used, with which the doctor picks up the hard stone located under the gums. This procedure is used quite rarely and mainly as an addition to ultrasonic cleaning,
- chemical removal: in the presence of very hard and abundant tartar, the doctor may resort to an acid-breaking procedure. This is a rather risky operation - if the acid gets on the gums or enamel, a burn may occur. However, sometimes chemical removal is the only way to get rid of solid deposits,
- laser: the most modern and safe, but expensive way to combat dental plaque. The laser not only effectively removes even hard stone, but also simultaneously allows for antibacterial cleansing of the oral cavity, significantly strengthening the enamel and inflamed gums.
2. Surgical cleaning of gum pockets
Often, professional teeth cleaning may not be enough and a surgical operation called will be required. It is necessary in the presence of voluminous gum pockets, when plaque and tartar are located deep under the gums and neither ultrasound nor laser simply “reaches” such remote areas. In addition, the doctor carries out the cleaning almost blindly, not seeing how deep the deposits are located.
The purpose of curettage is to remove gum pockets. The doctor has an important task - to make sure that the gums fit tightly to the tooth again, and there are no conditions for the re-development of infection. Curettage is performed under local anesthesia.
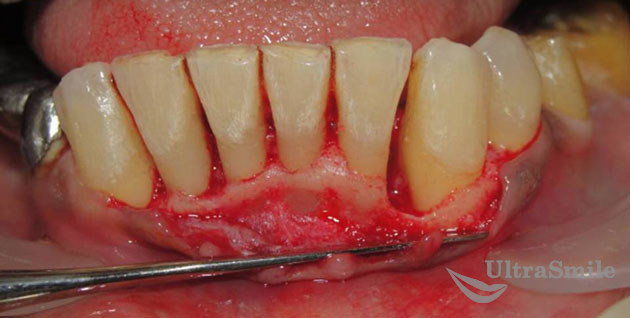
Simultaneously with open curettage, a flap operation can be performed, the purpose of which is to correct the position of the enlarged gum.
Video: closed gum curettage
3. Drug therapy
Carried out to relieve inflammation. Local remedies are used (rinses, compresses, baths), as well as general effects (medicines). For rinsing, medicinal solutions are used that reduce inflammation and eliminate pathogenic microflora (Chlorhexidine, Miramistin). Herbal decoctions (oak bark, chamomile, sage), which effectively eliminate bleeding gums, and ointments (Metrogil Denta) also help well.
 Herbal infusions can effectively combat gum inflammation
Herbal infusions can effectively combat gum inflammation An integral part of treatment is also taking antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve inflammation and eliminate pathogenic microbes.
4. Physiotherapy
The combination of drug therapy and physiotherapy also gives fairly good results in the treatment of periodontitis. To relieve inflammatory processes, reduce pain and bleeding, ultraviolet light, magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, darsonvalization and massage are used. As for massage, it can be performed both in a clinic (vacuum method) and independently. You can massage your gums with your finger in a circular motion, with a soft toothbrush, or by directing a weak stream of irrigator.

One of the most popular physiotherapy procedures is ultrasound – “Varius” is also used for this. They allow you to simultaneously remove dental plaque and heal soft tissues.
The purpose of this procedure is to strengthen mobile teeth to prevent their loss. Loose teeth are combined into groups with healthy ones - for these purposes, a fiberglass thread or splint is used, which is fixed on the inside of the teeth in a pre-prepared groove. The thread is covered with a composite material on top, so it becomes completely invisible - it is not felt and does not cause discomfort.
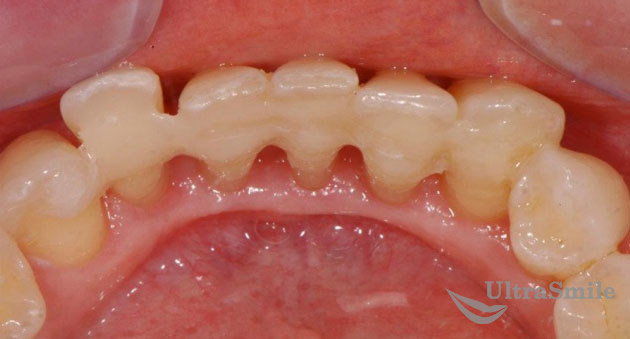
If a certain number of teeth are missing in the oral cavity, then removable clasp dentures can play the role of a splint. They are equipped with a metal base and hooks - unlike soft nylon ones, such dentures have a strong design, which allows them to be used simultaneously to replace lost teeth and fix mobile ones.
Video: splinting teeth
6. Careful hygiene
As we mentioned at the beginning, periodontitis in most cases occurs due to poor care of teeth and gums. Therefore, in order to maintain the results of the treatment, it is important for the patient to regularly, correctly and carefully care for his teeth and gums, especially since this is not at all difficult.
You need to use the brush and paste 2 times a day: in the morning before breakfast and in the evening after all meals. The brush should have medium-hard bristles, even if you have inflamed gums - too soft simply won’t cope with plaque. During the treatment of periodontitis, it is worth using special medicinal pastes that help reduce the signs of gum inflammation. After 1-2 months they should be changed to preventive ones.
 Oral hygiene is the key to healthy teeth and gums
Oral hygiene is the key to healthy teeth and gums After eating, you need to use dental floss and rinse, otherwise food debris will turn into plaque, causing inflammation. Using an irrigator will be useful - at home, it allows you to do an excellent job of cleaning the interdental spaces and even massage the gums, restoring metabolic processes in the tissues.
To maintain oral health, you must not only take care of your teeth and gums yourself, but also have them professionally cleaned 1-2 times a year. This will get rid of accumulated plaque and will be an excellent prevention of relapses of periodontitis.
In order to speed up the healing process of gums and bone tissue, reduce the manifestations of inflammation, and activate cell growth, so-called platelet injections are used, which are created on the basis of the patient’s blood.
7. Dental implantation for periodontitis.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely cure periodontitis and the disease will periodically return with new intensity. Losing teeth is inevitable, it’s only a matter of time - you may have to resort to an unpleasant procedure after decades, but there are situations when, due to tissue destruction, it is impossible to fix the teeth and the easiest way is to remove them. Naturally, after this the question of prosthetics arises. For a long time it was believed that implantation and periodontal inflammation are incompatible things. However, today dental implantation is carried out quite successfully even in cases of acute periodontitis, and often it is the replacement of natural teeth with artificial analogues that allows you to get rid of the manifestations of the disease forever. In case of tissue inflammation, it is worth choosing methods with immediate loading of the prosthesis, since the implants in this case are fixed in the deep parts of the bone (they are not subject to inflammatory processes). And after installing artificial teeth and chewing load (it becomes possible the very next day after installing the implants), metabolic processes in the jaw bone and gum tissue are restored.
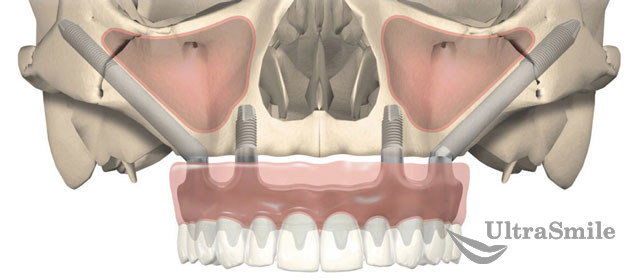 Dental implantation with Nobel Zygoma implants
Dental implantation with Nobel Zygoma implants As you can see in the picture, with periodontal disease in the upper jaw, patients may be offered the option of zygomatic implantation. This technique involves, in addition to the implantation of classic implants using the spongy layer, several zygomatic models, incredibly long, but at the same time very effective. You can notice that they bypass the nasal sinuses at an angle, and are attached to the cheek bone, which is very strong and protected from any inflammation. On the same day, a permanent, functional prosthesis is fixed on them, ensuring the stability of the entire structure with the help of a metal component.
As for the treatment of periodontitis at home, rinsing with medicinal herbs is quite acceptable. But this in no way can be a substitute for professional treatment - self-medication may alleviate the condition a little, but it will not get rid of the inflammatory process, which means tissue infection will continue to progress.