Where does the duodenum hurt?
Where does the duodenum hurt? I wonder who suddenly has a stomach ache. Where is it located and what role does it play in the body?
Why is it needed, how and where does the duodenum hurt:
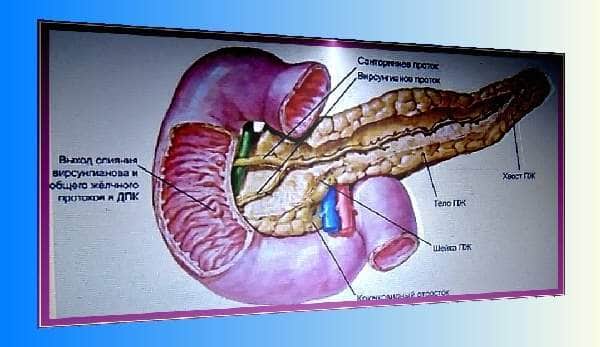

Let's look at a simple example:
- You ate at lunch, it doesn’t matter what, just a big meal. The food you eat will stay in your stomach for about 6 to 8 hours.
- In portions it begins to accumulate in the upper part of the stomach. Then it is mixed and placed in layers.
- We must not forget about moderation in eating. It is possible if you eat food hastily.
- Then it passes in small portions into the small intestine, connected to the stomach. The small intestine begins with the duodenum.
- But in it, with the help of juices produced by the pancreas, its enzymes, bile coming from the liver, the breakdown of food begins.
- Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are actively processed.
- All walls of the duodenum are covered with a large number of villi. They all have their own blood vessels, capillaries.
- Well-broken substances are absorbed in them: such as glucose, amino acids, glycerol.
- Digestion occurs throughout the entire length of the small intestine.
- Undigested food remains move into the large intestine within 12 hours. This is where most of the water absorption occurs into the blood.
- It is twelve fingers long. If something doesn’t work in this area, all digestion is disrupted.
Parts of the duodenum:
- Upper part (level of the first lumbar vertebra). It is also called onion due to its round shape. Length five, six centimeters.
- Descending part (descends to the third lumbar vertebra).
- Horizontal part (level of the third lumbar vertebra).
- Ascending part (ascends to the second lumbar vertebra).
Bends are visible between the sections of the intestine:
- Top bend.
- Bottom bend.
- The junction of the duodenum and the jejunum.
Where is the duodenum located and how does it hurt:
The duodenum is located in the epigastric region, above the navel. Presses on the anterior abdominal wall.
To be precise, it surrounds the pancreas in a “horseshoe” shape.
Two ducts flow into the intestine from and also from the pancreas. This place is considered the main one; all digestive enzymes go here. Amylase, lipase, protease begin the breakdown of food.
Based on this, there are five forms of duodenum:
Forms of the duodenum:
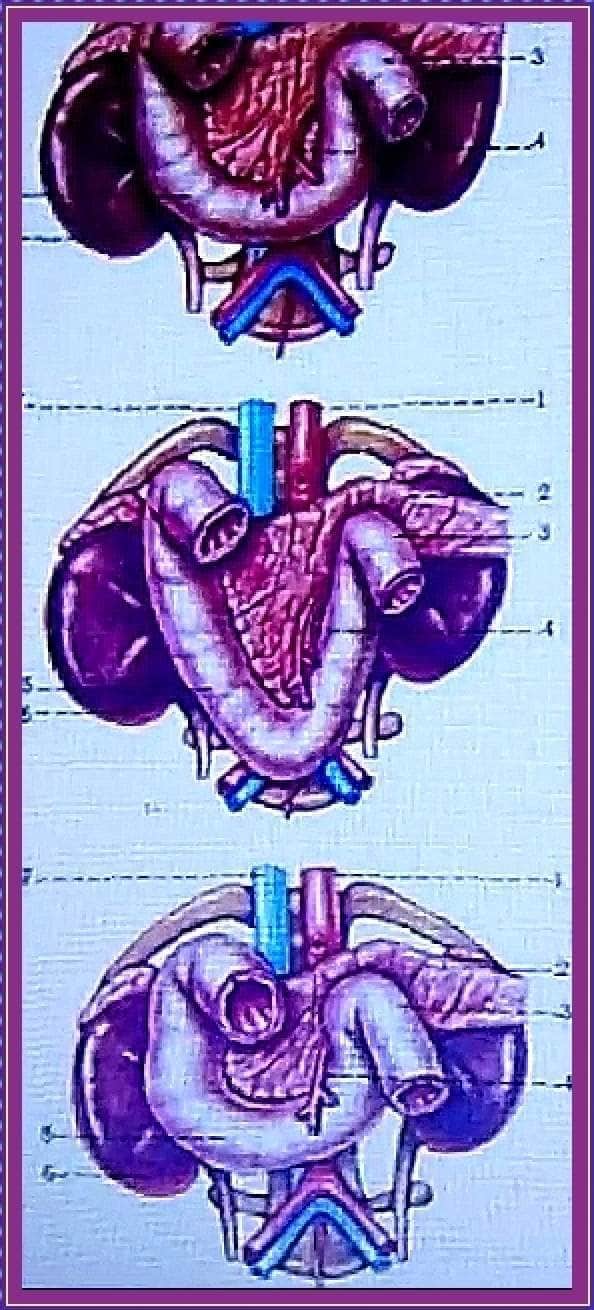

- Up to 60% - horseshoe shape.
- Up to 20% - folded form.
- Up to 11% - V - shaped.
- Up to 3% - C - shaped.
- Up to 6% - ring-shaped.
The structure of the wall of the duodenum:
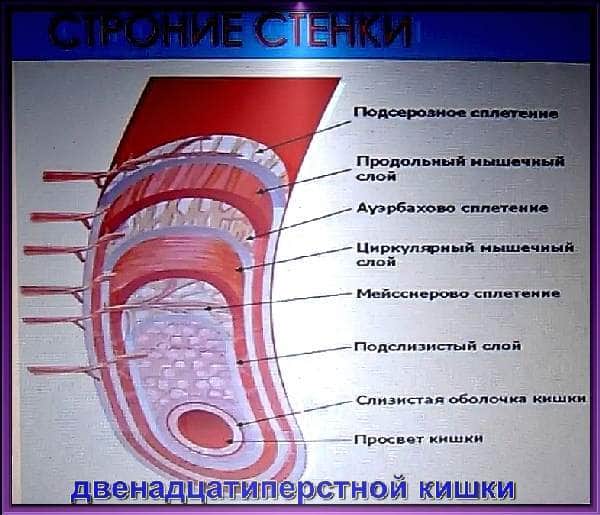

- The mucous membrane itself (absorption of fats, amino acids, glucose).
- Submucosa.
- Muscular layer (motor-evacuation function).
Where does the duodenum hurt, causes of pain:
The duodenum is almost the first to pay for our nutritional disorders, poor water quality, our stress, and the eternally depressed state of the body.
There are a very large number of different nerve receptors here. They need normal blood supply and nutrition.
When there are failures, everyone suffers, including the duodenum.
Bowel diseases can be caused by:
- Diabetes.
- Cholelithiasis.
- Heredity.
Inflammatory process of the duodenum:
The so-called duodenitis.
Where does it hurt with this disease:
- Or on the right side just below the ribs (dull pain).
- Nausea.
- Or in the epigastric region.
- After eating, the stomach expands to the sides
- Vomit.
- Refusal of food
- weight loss.
The development of duodenitis (or inflammation of the gallbladder) or pancreatitis (inflammation) is dangerous. It is not uncommon for an ulcer to develop.
All these organs are located nearby and communicate with each other. They usually say that these organs get sick together.
The cause of intestinal inflammation may be:
Any viral infection: (Helicobacter pylori) is the most known to us.
When diagnosed, treatment is prescribed:
- Antibiotics (only with a doctor’s prescription, taking into account all tests). They are treated for two weeks to destroy the infection.
- Proton pump inhibitors are prescribed along with antibiotics to protect the intestinal and gastric mucosa.
- Antispasmodics: dratoverine, but - spa, papaverine.
- Anthracites to reduce pain and acidity in the intestines: almagel, omeprazole.
- Maalox is prescribed for intestinal dysfunction.
- Physiotherapy: magnetic therapy, ultrasound, paraffin therapy, heating.
Foods that increase the production of stomach acid are removed from the diet.
Food is received warm. Meals are frequent, in small portions.
Forbidden:
- Fatty, fried foods, broths.
- Sour fruits.
- Spices (pepper, vinegar, salt, mustard).
- Alcohol, nicotine.
- Freshly squeezed fruit and vegetable juices.
- Smoked, salted products.
- Mushrooms.
- Pickled foods.
- Carbonated sweet drinks.
- Coffee Tea.
- Vegetables, fruits in raw form.
- Legumes.
Allowed:
The food is prepared steamed or boiled.
- Vegetable fats (olive, sunflower oil).
- Slimy, boiled soups.
- Boiled lean meat (chicken, turkey).
- Boiled fish.
Bowel cancer:
This is not a rare disease these days.
Early symptoms:
The pain is felt immediately on the right side, just under the ribs, spreading to other organs.
- You become constipated and are forced to take laxatives.
- Blood in the stool during defecation. Don’t be disdainful, look into the toilet - this is the work of your body.
- Blood should be red if present (black or cherry color is also possible).
- Constant urge to defecate. You went to the toilet, but you need to go there again, even though there is no chair.
- There is a narrowing of the anus.
- Gas begins to form and the stomach swells.
- Jaundice, fever.
- Itching of the skin (high bilirubin in the blood, skin receptors are irritated). Constant itching leads to insomnia and irritation.
If these symptoms appear and concern you, do not delay the examination. It saves lives.
Treatment begins with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. The size and method of surgical intervention depends on the stage of the disease (organ damage) of the sick person.
Duodenal ulcer where it hurts:
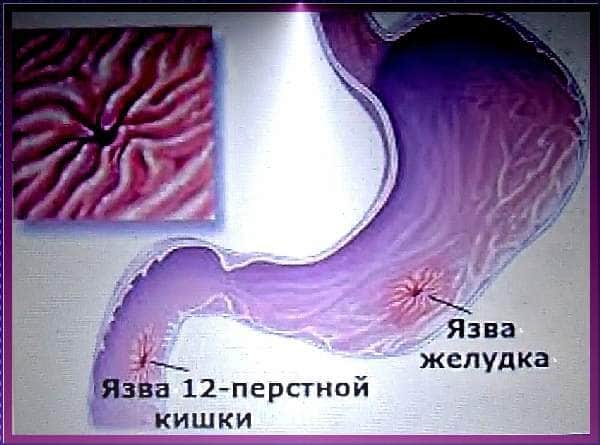

Usually develops in the area of the duodenal bulb.
- There is a clear disorder in digestion.
- I suffer from frequent, loose stools.
- There is an absolute intolerance to dairy products.
- Yellow coating on the tongue (spasm of the bile ducts).
- The right side hurts, the pain is sharp to the point of exhausting aching. It happens in attacks or, on the contrary, for a long time.
- It radiates to the lower back or thoracic spine. In some patients, pain is felt in the collarbone area.
- Relief from pain is eating. Such pains are called “hungry pains”.
- Skin yellowish.
- Scars appear on sore areas of the mucous membranes.
- Nausea and vomiting.
The treatment is very serious and long-term. Prescribed after a complete examination for life.
- In order to destroy Helicobacter pylori, antibiotics are taken (erythromycin, metronidazole).
- To reduce the formation of hydrochloric acid - omeprazole.
- The administration of anthracite reduces pain.
Where does the duodenum hurt, diagnosis:
- A gastroscopy is prescribed using an endoscope with a small television camera at the end. It is administered through the mouth into the stomach, then into the duodenum.
- An endoscope is used to examine the intestinal mucosa, find diseased areas, and take a small piece for analysis (biopsy).
- Determine the cause of the disease for adequate treatment.
Dietary nutrition is of great importance in the treatment and recovery of the patient. Serious reduction in cases of exacerbations of the disease, improvement of the patient’s well-being.
Get diagnosed in a timely manner to identify Helicobacter pylori and get treatment. It is possible without treatment.
Follow a daily routine and rest in moderation. Try not to eat unhealthy foods, your body will thank you.
And I wish you and your family health!
Check me out more often.
Watch the video, all about the duodenum: