What does E. coli say in a smear?
May take part in digestive metabolic processes. However, there are some in its family that can cause serious infections in the abdomen, intestines, lungs, urinary tract and brain.
Causes
Basically, E. coli infection occurs through contact with infected people and poor personal hygiene. It can be transmitted by water and nutrition. In the first case, pathogenic E. coli enters the body if you drink unboiled water. In the second case, the source of infection is inseminated food.
Where is she from
-Escherichia coli in women. There are cases when female representatives may have E. coli in a vaginal smear. This is a sign of bacterial vaginosis, which begins with a yellow or brown foul-smelling vaginal discharge. In this case, the occurrence of the disease is due to lack of personal hygiene.
- Escherichia coli in urine. The appearance of this indicator is the most common cause of cystitis in women. In this case, there is a high probability of penetration of conditionally pathogenic microflora into the ureter and bladder. Here, E. coli in the smear becomes a hostile pathogenic agent, causing very severe inflammation, changes in the integrity of the mucous membranes, frequent urination, burning, and pain.
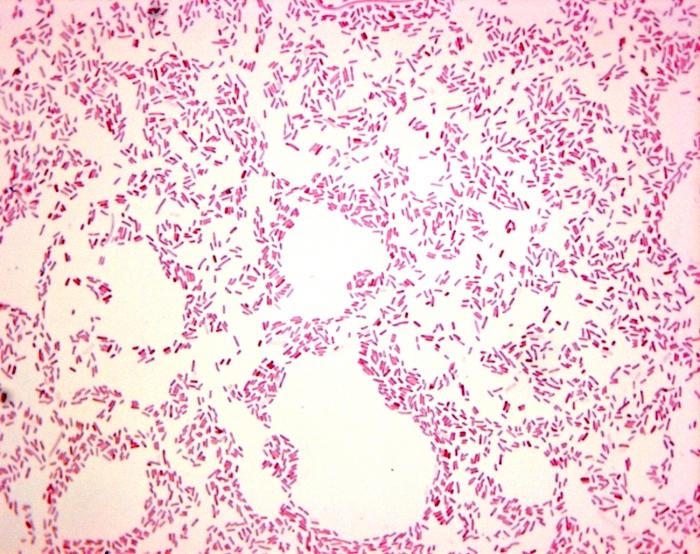
Types
- Enterotoxigenic. This E. coli in the smear is the cause of tourists' diarrhea. Causes mild illness accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea.
- Enteropathogenic. The main source of diarrhea in children is precisely these E. coli bacteria in the smear. Bacteria attach to the small intestine and destroy it and microvilli, which affects the absorption of water and nutrients from the intestine.
- Enteroinvasive. This E. coli causes a disease called dysentery. The most common symptoms are abdominal pain and severe watery diarrhea. Bloody stools are possible, and in severe cases, green vomit and increased body temperature are added. E. coli in infants can cause electrolyte imbalance and dehydration.
- Hemolytic. This is the most dangerous type, the effects of which can cause paralysis of the smooth muscles of the intestines and stomach. Such E. coli in the smear has a negative tendency to upset the mucous membrane in the colon and cause bloody diarrhea.
Symptoms and signs
During the incubation period (1-7 days) there are no symptoms of infection. Later, the symptoms of E. coli can be expressed:
Severe diarrhea;
Vomit mixed with greens;
Increased body temperature;
Lethargy and loss of appetite;
Nausea;
Nagging pain in the abdomen.
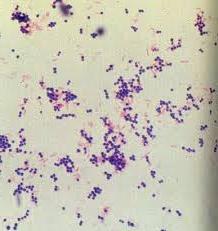
If you are infected with E. coli, drinking plenty of fluids is recommended, including a solution of the drug “Regidron”, and the drug “Smecta” is also prescribed. Active antibacterial therapy is possible. It is necessary to follow a diet that excludes fatty and fried foods.